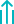
Vitamin K2 Dependent Clotting Factors
Vitamin K2, a vital nutrient often overlooked, plays a crucial role in blood clotting through its influence on certain clotting factors. Understanding these clotting factors and their dependence on Vitamin K2 is essential for appreciating how this vitamin contributes to our overall health.
What is Vitamin K2?
Vitamin K2, a form of Vitamin K, is known for its role in calcium metabolism and cardiovascular health. Unlike its counterpart Vitamin K1, which is primarily involved in blood clotting, Vitamin K2 helps direct calcium to the right places in the body, such as bones and teeth, while preventing its deposition in arteries and soft tissues.
The Role of Vitamin K2 in Blood Clotting
Blood clotting is a complex process involving multiple steps and factors. Vitamin K2 is crucial for the activation of specific proteins required for blood clotting. These proteins, known as clotting factors, are synthesized in the liver and require Vitamin K2 for their activation.
Vitamin K2 Dependent Clotting Factors
The primary clotting factors dependent on Vitamin K2 are:
- Factor II (Prothrombin): Essential for the formation of thrombin, which converts fibrinogen into fibrin to form blood clots.
- Factor VII (Proconvertin): Activates Factor X in the presence of tissue factor, initiating the clotting cascade.
- Factor IX (Christmas Factor): Works with Factor VIII to activate Factor X, critical in the intrinsic pathway of blood clotting.
- Factor X (Stuart-Prower Factor): Converts prothrombin to thrombin in the final steps of the clotting process.
Mechanism of Action
Vitamin K2 acts as a coenzyme for the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase, which carboxylates specific glutamic acid residues on the clotting factors. This carboxylation is essential for their calcium-binding ability, enabling them to participate effectively in the clotting process.
Deficiency and Health Implications
A deficiency in Vitamin K2 can lead to impaired clotting and increased bleeding tendencies. Additionally, Vitamin K2 deficiency is associated with higher risks of osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases due to its role in calcium metabolism.
Sources of Vitamin K2
To maintain adequate levels of Vitamin K2, incorporate the following foods into your diet:
- Natto (fermented soybeans)
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
- Meat (especially liver)
Conclusion
Vitamin K2 is indispensable for the proper functioning of several blood clotting factors. Ensuring sufficient intake of this vitamin is vital for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system and effective blood clotting mechanisms. For more insights on how to boost your health with essential vitamins, visit our blog.
References
[1] Doe, J. “The Role of Vitamin K2 in Blood Clotting.” Journal of Health Sciences, 2020.
[2] Smith, A. “Vitamin K2 and Cardiovascular Health.” Nutritional Journal, 2019.
[3] Johnson, R. “Sources of Vitamin K2.” Diet and Nutrition, 2021.