

Change the way You
Think, Feel & Age
Our mission is to bring more wellbeing into the world. We empower people to live longer, healthier and happier lives.
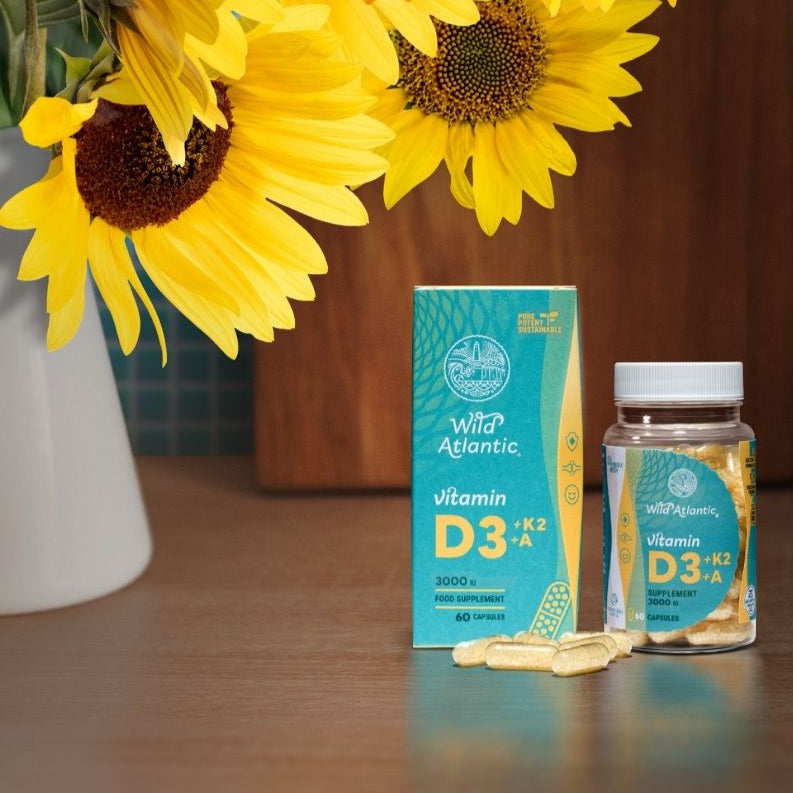


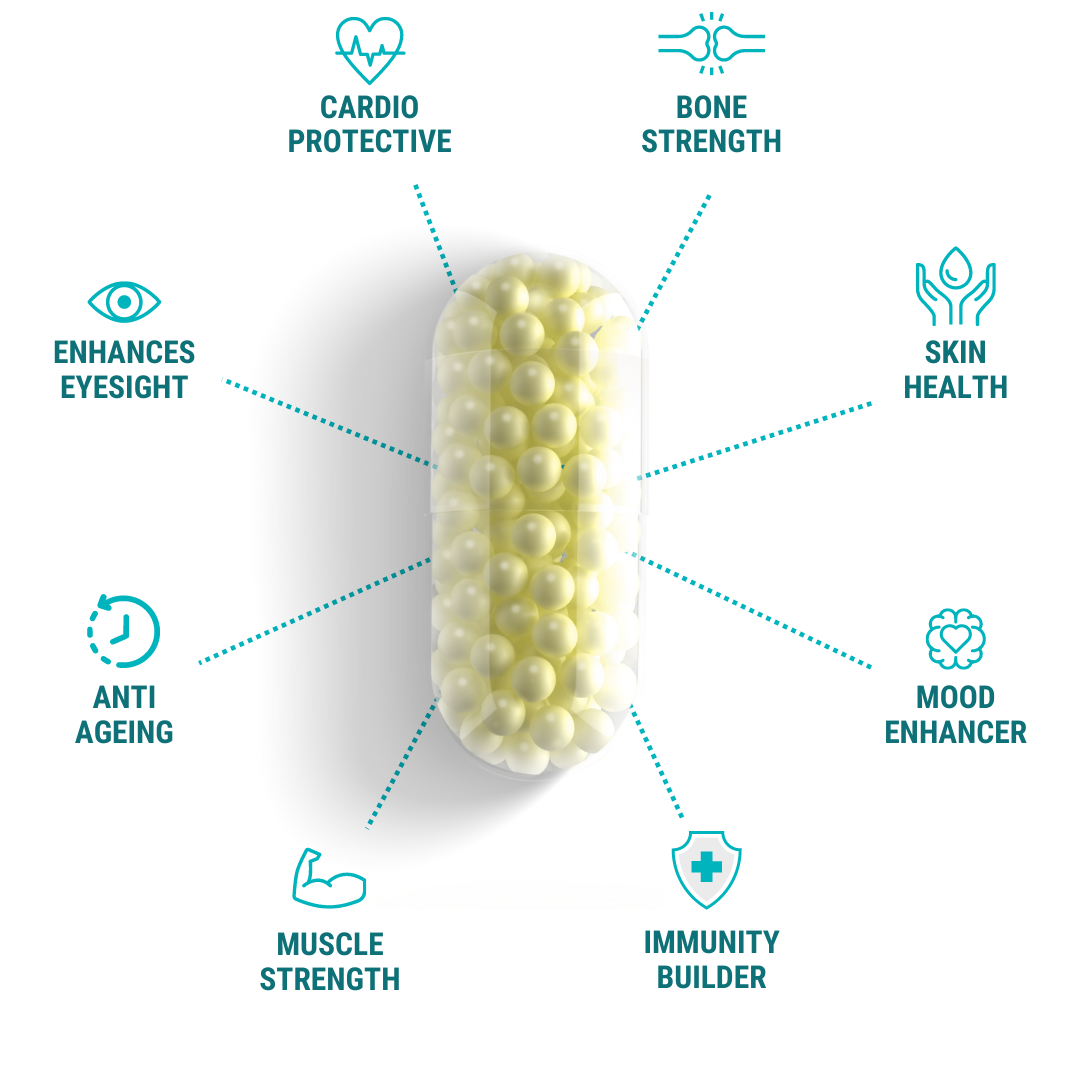
Vitamin D3+K2+A
3 in 1 power formulation to boost immune, bone, and cardiovascular health.

Free shipping over €70
More of what you need, delivered for free.
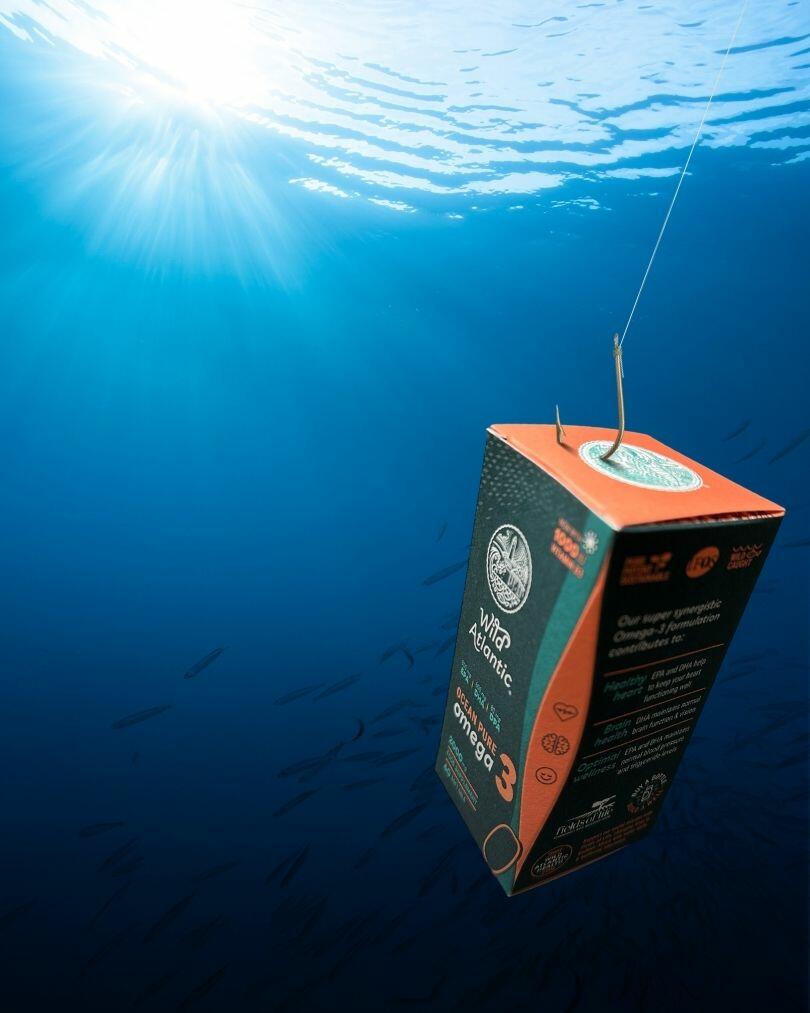

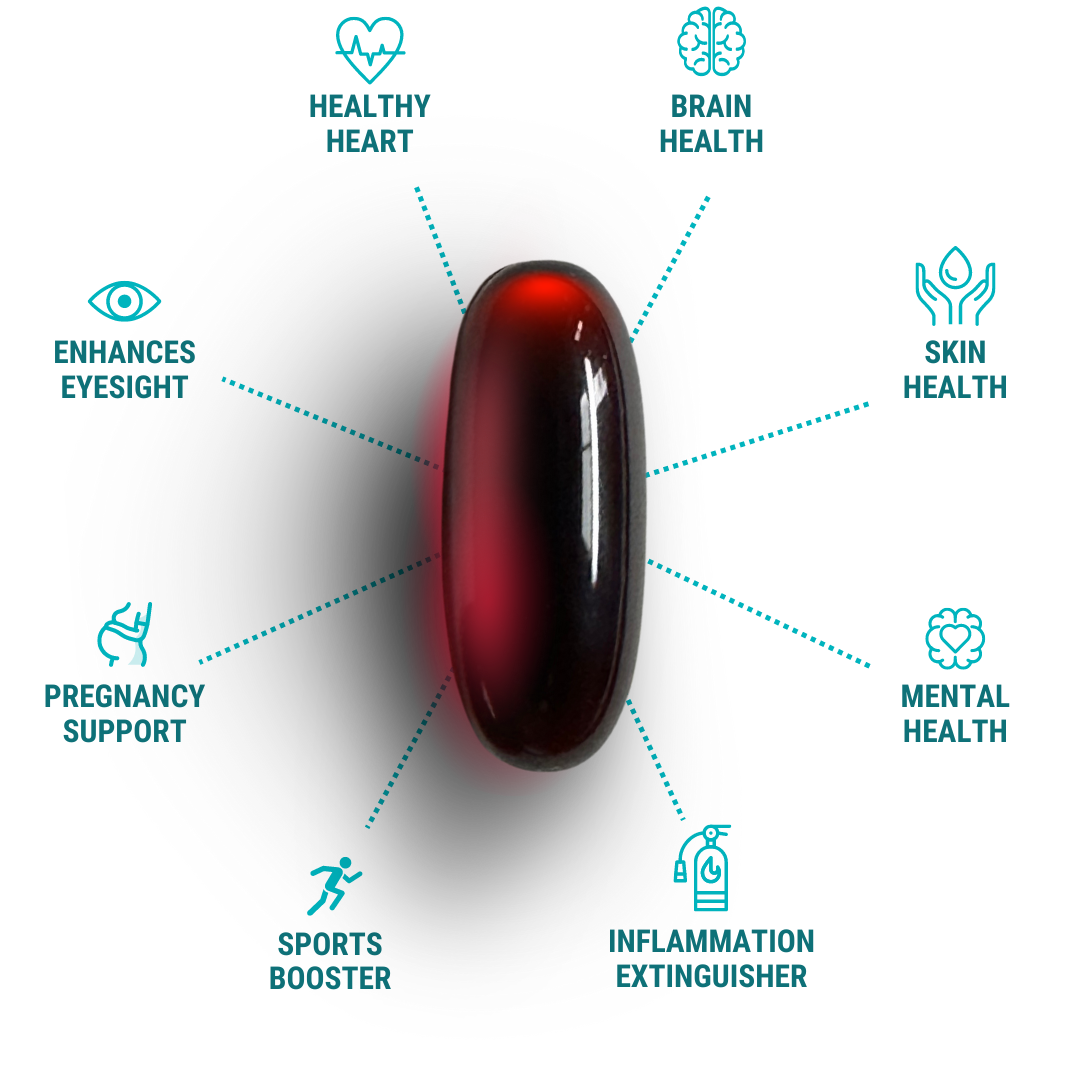
Ocean Pure Omega-3
Powerful blend of EPA, DHA & DPA for optimal heart, brain, and metabolic health
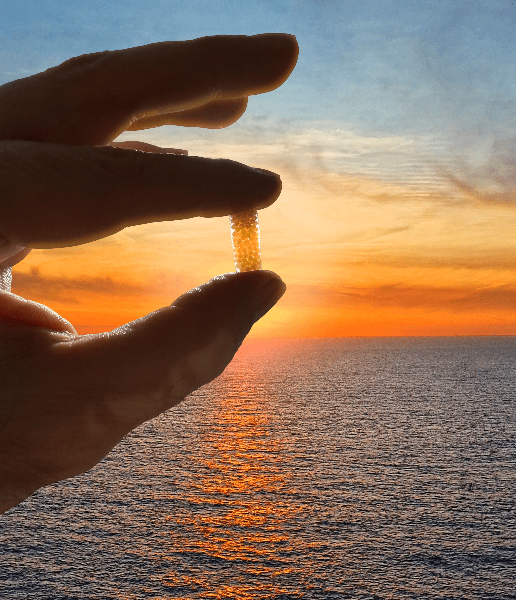

Good things come naturally...
One less thing to think about.
Save time, money, and mental energy with a simple supplement subscription.

Incredible Supplements!
I have noticed a significant difference in my body. I am feeling light and energetic and my sleeping patterns have improved drastically, even after taking them for the first month

Sustained health Made Easy
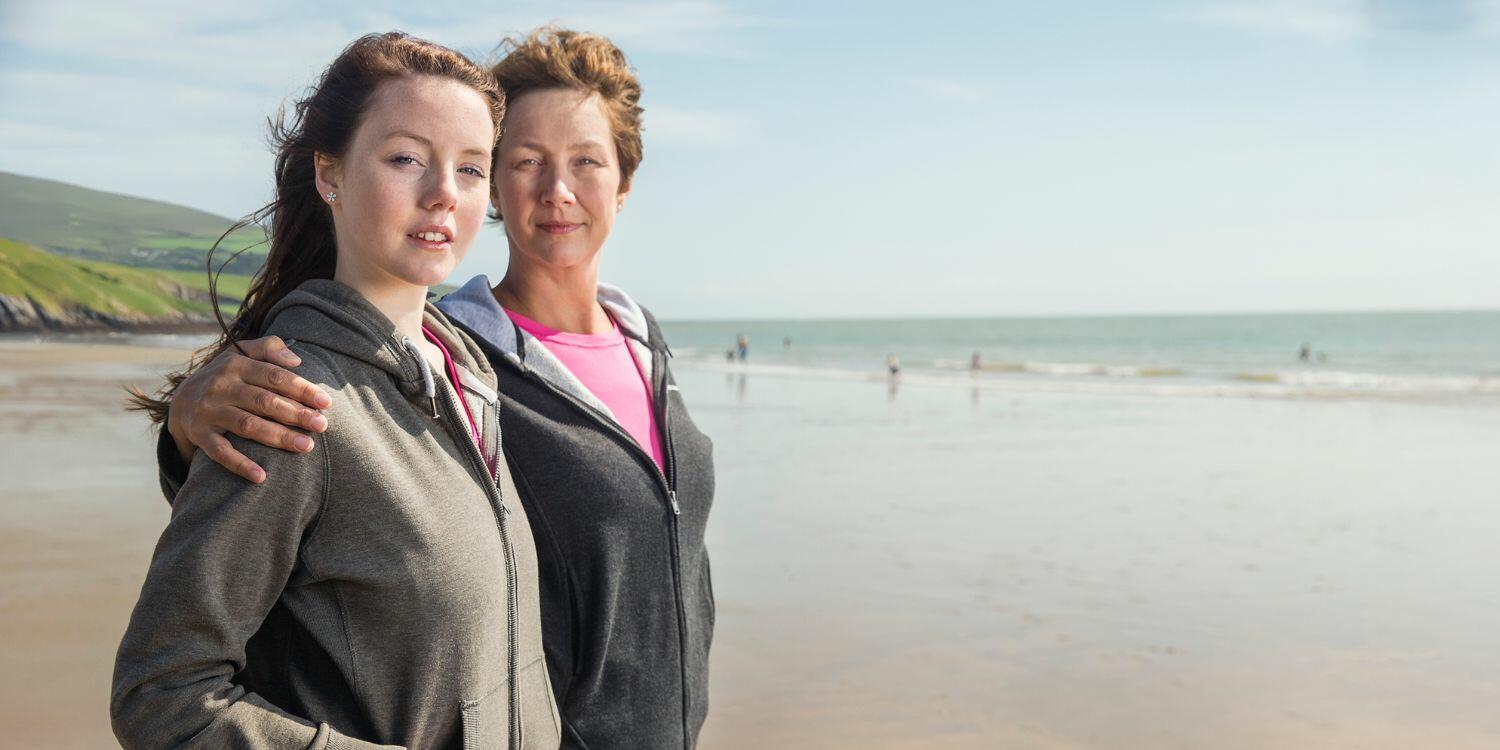






Stay Healthy,Rain or Shine
In Ireland we don't get enough sunshine. Our Vitamin D3+K2+A helps keep your immune system strong, energy levels up, and bones healthy—rain or shine.


Fuel Your Heart, Brain and Body
Ocean Pure Omega-3 supports your heart, sharpens your mind, and helps reduce inflammation—so you feel energised and balanced every day.
Sunshine
in a Bottle
When sunshine’s in short supply, Vitamin D3+K2+A keeps your immune system strong, your bones healthy, and your energy up—all year round.

Vitamin D3+K2+A
Triple-action support for heart, bone, and immune health.
The Mega
Omega
Supports heart, brain, and joint health while reducing inflammation and boosting overall wellbeing—so you feel your best, inside and out.

Ocean Pure Omega-3
A pure blend of EPA, DHA, and DPA to fuel your heart, mind, and metabolism—naturally.
Small Steps, Big Impact
Better sleep.
Daily walks.
Whole foods.
Smart supplements.
Small choices add up to lasting change.
Loved by Experts, Trusted by All
From nutritional therapists to new mums and fitness pros, Wild Atlantic is trusted by those who take their health seriously.


Omega 3.Fantastic quality, great Irish brand. Vitamin D3 K2 and A.. two of these capsules replaces 8 capsules I was previously taking. Big help! Highly recommend

I have been taking the Wild Atlantic D3+K2+A for over a year now and feel the benefits. It is great to have an Irish company where you can trust the high quality of their source and backs it up with a testing kit . Deliveries in a few days is a real bonus.

Know Your Numbers, Own Your Health
Measure key health markers like Vitamin D and Omega-3—without leaving home. Get doctor-approved lab results and personalised insights to guide your next steps.
Measure, understand, thrive
from the Comfort of Home

Simple Steps to Take Control of Your Health
Collect your sample, post it back for free, and get clear, personalised results within two weeks..
Test. Don’t Guess. Know exactly what your body needs to thrive.

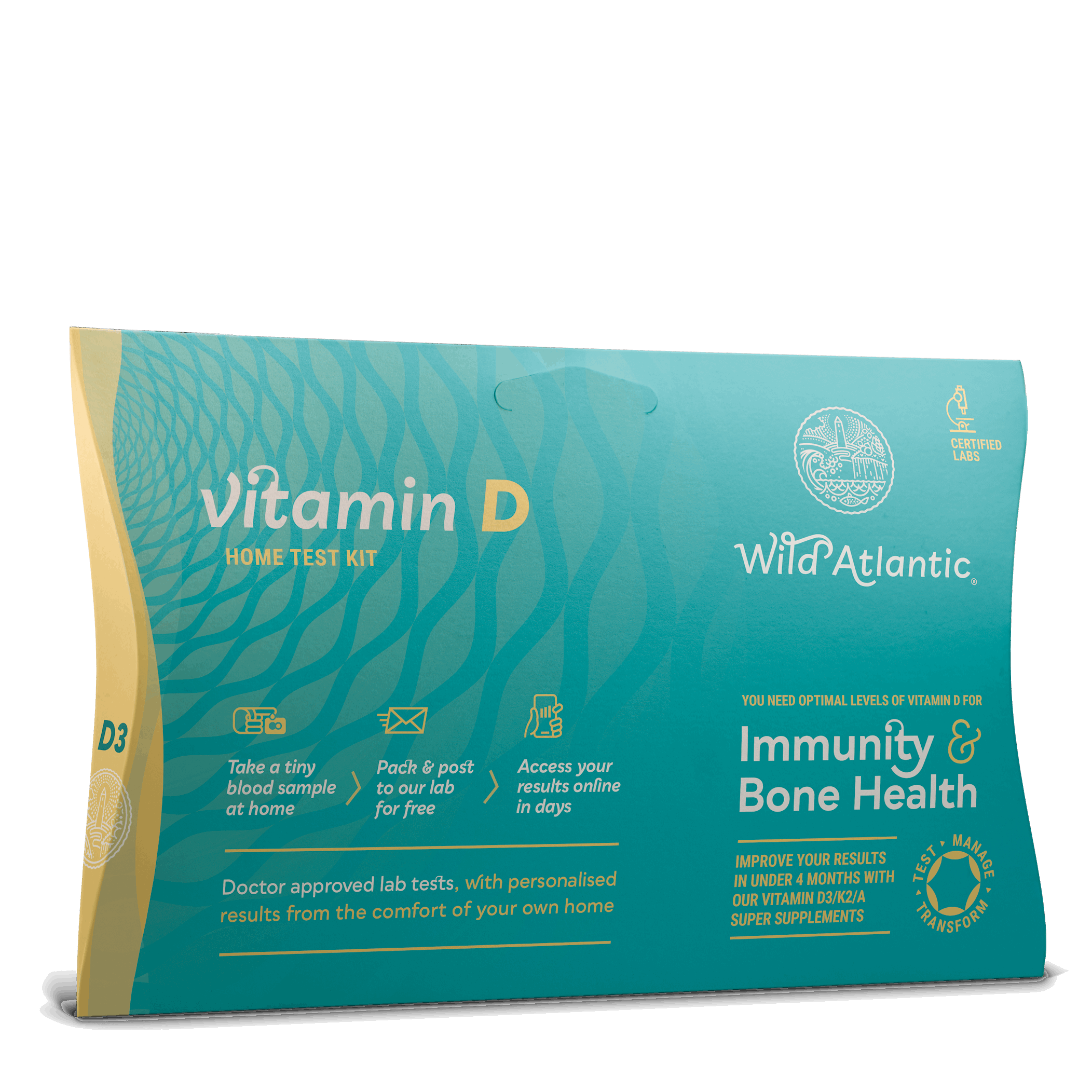
Vitamin D Test
Check your Vitamin D levels from home—for stronger bones, better immunity, and all-round health.

Omega-3 Essential Home Test
Measures your Omega-3 Index and provides insights into EPA, DHA, heart, and brain function.

Omega-3 Advanced Home Test
Our most comprehensive test—measuring 24 fatty acids including Omega-3, Omega-6, and trans fats.
Sustainably Sourced,
Thoughtfully MadeWe believe in health that cares for people and the planet. Rooted in Irish values, Wild Atlantic sources ethically, packages sustainably, and partners with Fields of Life for impact.
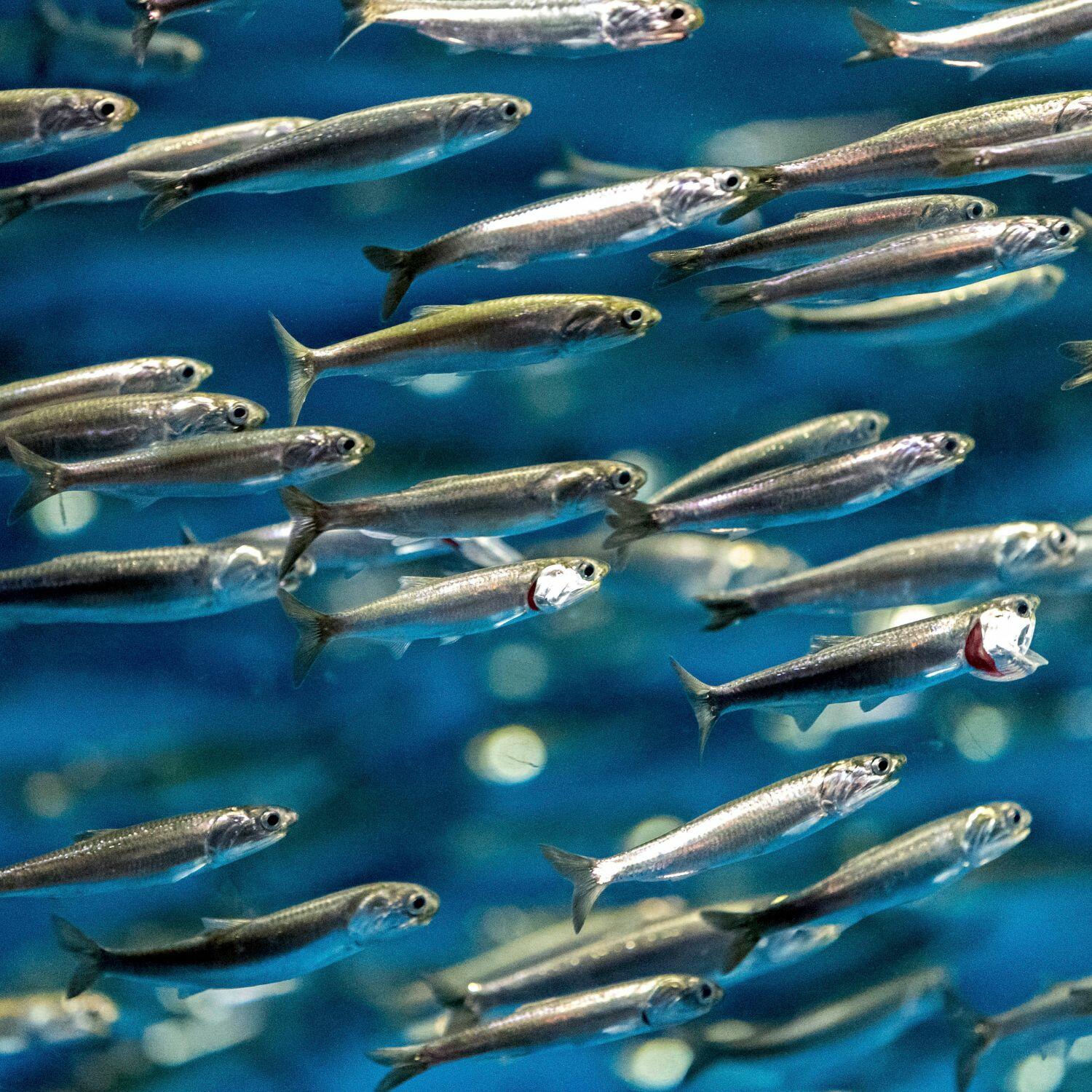

From Ocean To Bottle

Sustainably wild-caught anchovies with full traceability—protecting ocean life while delivering premium quality.
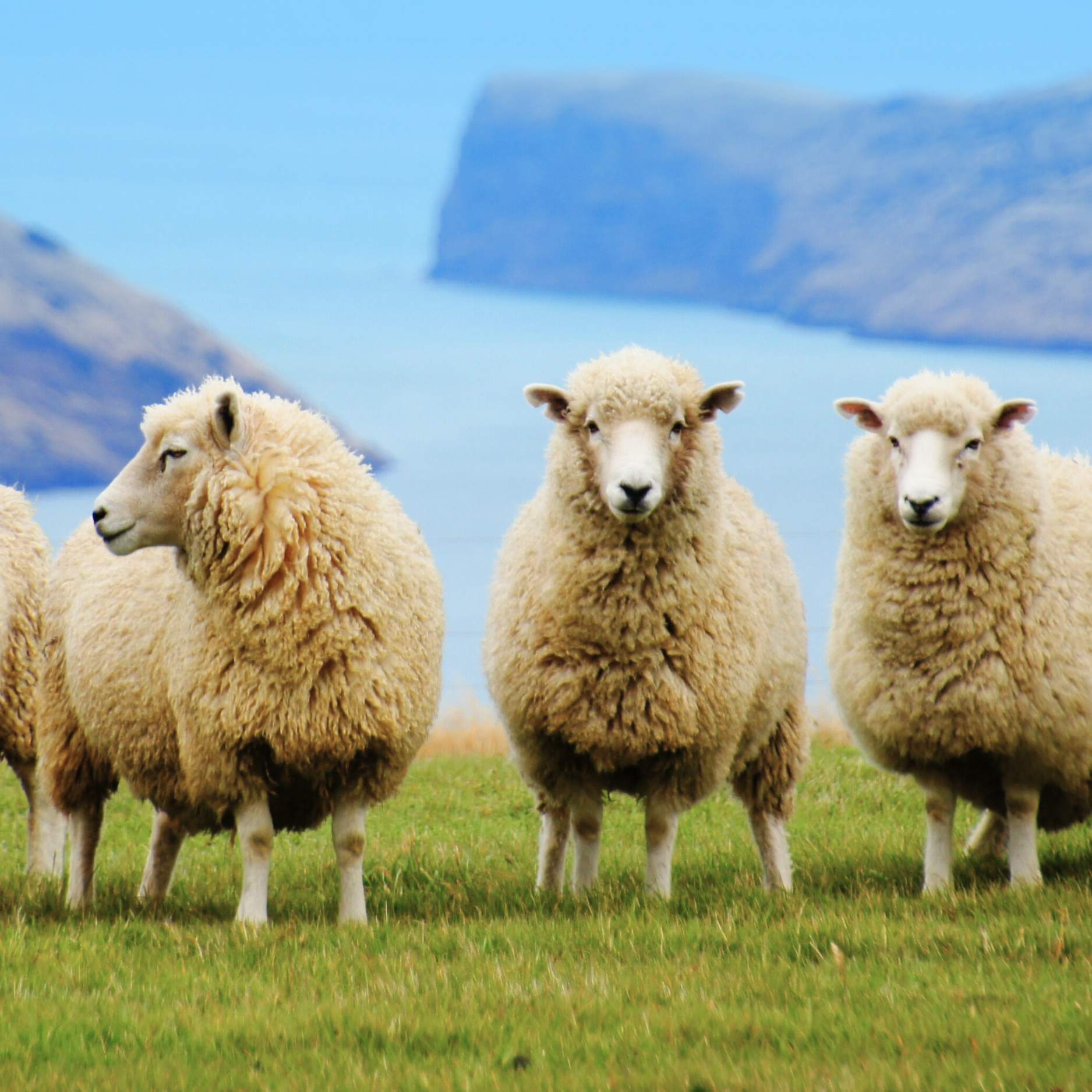

Sunshine from Sheep?

Our Vitamin D3 comes from lanolin—a renewable, natural source from sheep’s wool that’s gentle on both animals and the planet.

Supporting Local

We source locally whenever we can—supporting Irish communities and reducing our environmental impact.
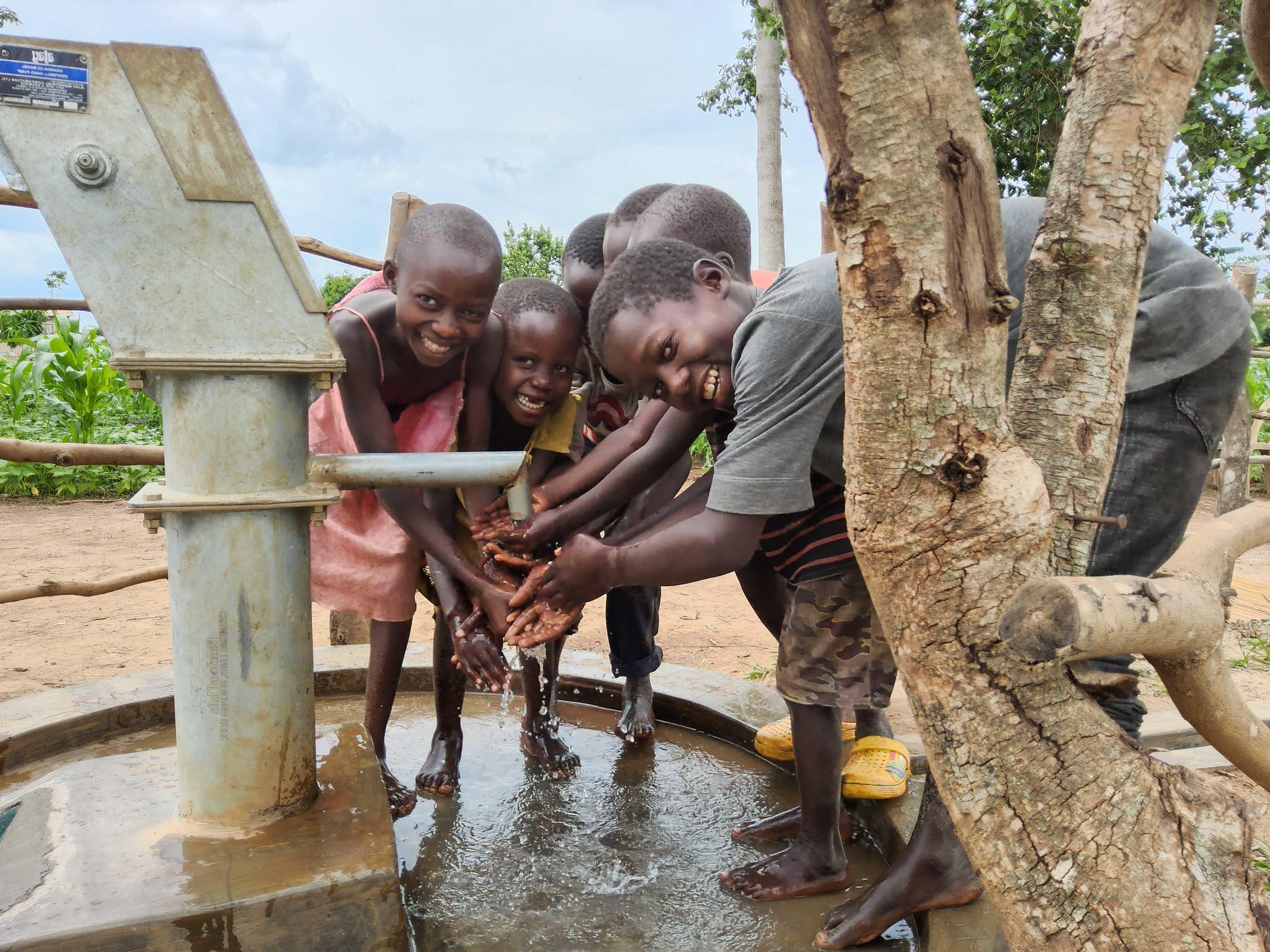

More than a Supplement

With every bottle, you’re helping build clean water wells in Africa through our ‘Buy a Bottle, Build a Well’ initiative, supporting communities in need.
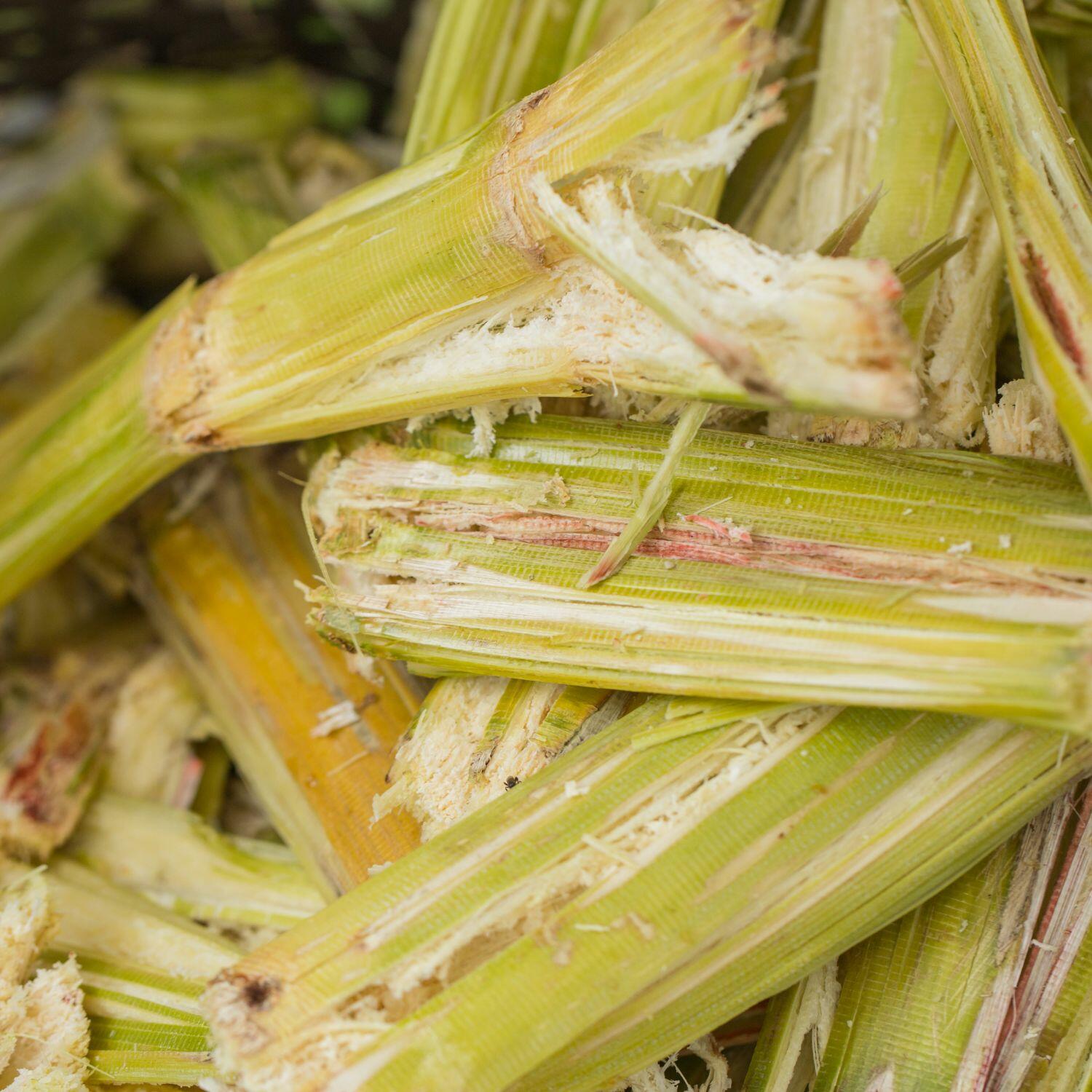

Eco-Friendly Packaging

Our bottles are made from sugarcane bagasse, a renewable, biodegradable alternative to traditional plastic, helping reduce environmental impact.

BIODEGRADEABLE & COMPOSTIBLE BOTTLES
LOWER CARBON FOOTPRINT THAN GLASS BOTTLES
LOWER CARBON FOOTPRINT THAN CONVENTIONAL PLASTIC BOTTLES
Explore Health Naturally
We’ve answered your most common questions and shared expert insights to help you thrive. Whether you’re curious about supplements or sustainable living, we’ve got the information you need to make confident, healthy choices.
FAQs
How does omega-3 improve brain, heart, and joint health?
Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, support brain function, enhance mood, and improve memory. They reduce inflammation, regulate heart rhythm, lower triglycerides, and promote flexible joints, easing discomfort. Regular omega-3 intake contributes to long-term cardiovascular, cognitive, and joint health.
Why is sustainable sourcing important for supplements?
Sustainable sourcing ensures that ingredients, like wild-caught fish, are harvested responsibly without harming ecosystems. It reduces environmental impact, supports biodiversity, and guarantees traceable, high-quality products. Sustainable practices also align with consumer values, contributing to both individual and planetary health.
How do I know if I need a vitamin D or omega-3 test?
If you feel fatigued, experience low immunity, mood swings, or inflammation, or if your diet lacks sun exposure and fish, a home test can reveal deficiencies. Personalised test results ensure you take the right supplements to address your unique health needs.
Can I take your supplements while pregnant or breastfeeding?
Yes, our supplements are designed with natural ingredients, but we recommend consulting a healthcare provider to ensure safety and the right dosage for pregnancy or breastfeeding. Proper supplementation during this time supports maternal and infant health.
What makes your supplement packaging eco-friendly AND biodegradable?
Our packaging uses sugarcane bagasse, a biodegradable and renewable material that reduces emissions. Compared to plastic, it has a 75% lower carbon footprint, and it’s fully compostable, ensuring sustainability. We aim to protect the environment with every product we offer.
How do subscription plans work, and what are the benefits?
Our subscription plans provide convenience and savings, with up to €50 off monthly orders and free delivery. Subscribers can pause or cancel anytime, ensuring flexibility. This option ensures consistent supply, removes hassle, and helps you maintain your health routine effortlessly.
From Our Blog

Vitamin D Calculator: How to Easily Find Your D...
Millions of people—especially those living in northern climates—are unknowingly deficient in vitamin D. If you work indoors,...
Vitamin D Calculator: How to Easily Find Your D...
Millions of people—especially those living in northern climates—are unknowingly deficient in vitamin D. If you work indoors,...
Read More
Omega 3 and Its Effect On The Immune System
Omega-3 fatty acids, essential nutrients found in various foods and supplements, are well-known for their numerous health...
Omega 3 and Its Effect On The Immune System
Omega-3 fatty acids, essential nutrients found in various foods and supplements, are well-known for their numerous health...
Read More
Follow Our Podcast
Check out HealthWaves, the podcast that dives into holistic health and wellness. Meet Eilis Ó Broin, our host and nutritional therapist. Each episode, we explore topics like nutrition, exercise, mental health, and more, offering expert advice and inspiring stories to help you live a vibrant, balanced life.
Let’s get started on our journey to feeling wildly healthy!

